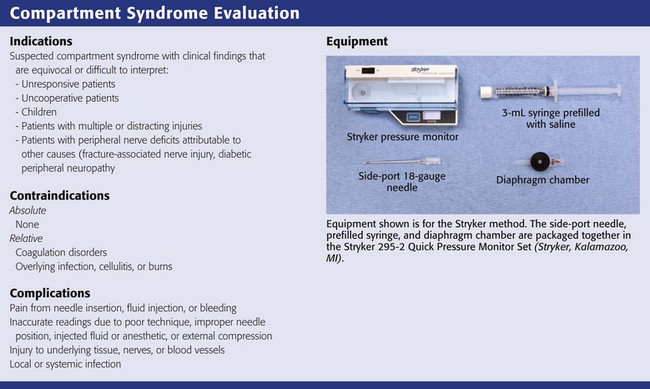
Compartment Syndrome Pressure Monitoring
Compartment syndrome pressure monitoring. Normal compartment pressures are less than 8mmHg. We first review how to setup and use the Stryker intracompartmental pressure monitor device then we review the anatomical compartments and where to insert t. Monitoring and a threshold of diastolic blood pressure minus intracompartmental pressure 30 mmHg to assist in ruling out acute compartment syndrome.
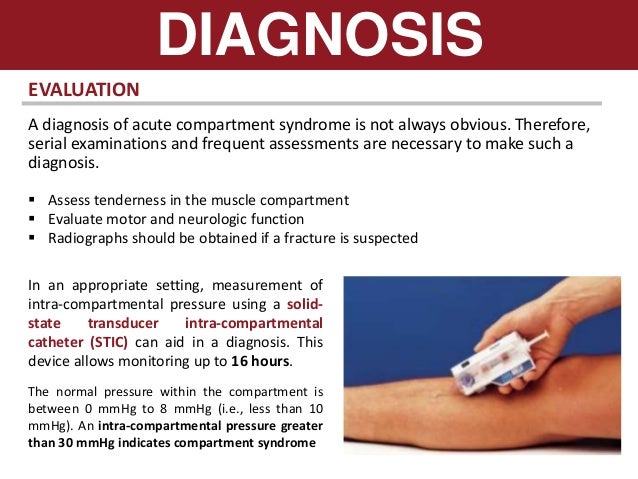
To check the number of remaining measurements. If the diagnosis is clear then the patient must undergo urgent fasciotomies. Systematic review and recommendations for intracompartmental pressure monitoring in diagnosing chronic exertional compartment syndrome of the leg Studies in which an independent blinded comparison is made with a valid reference standard among consecutive patients are yet.
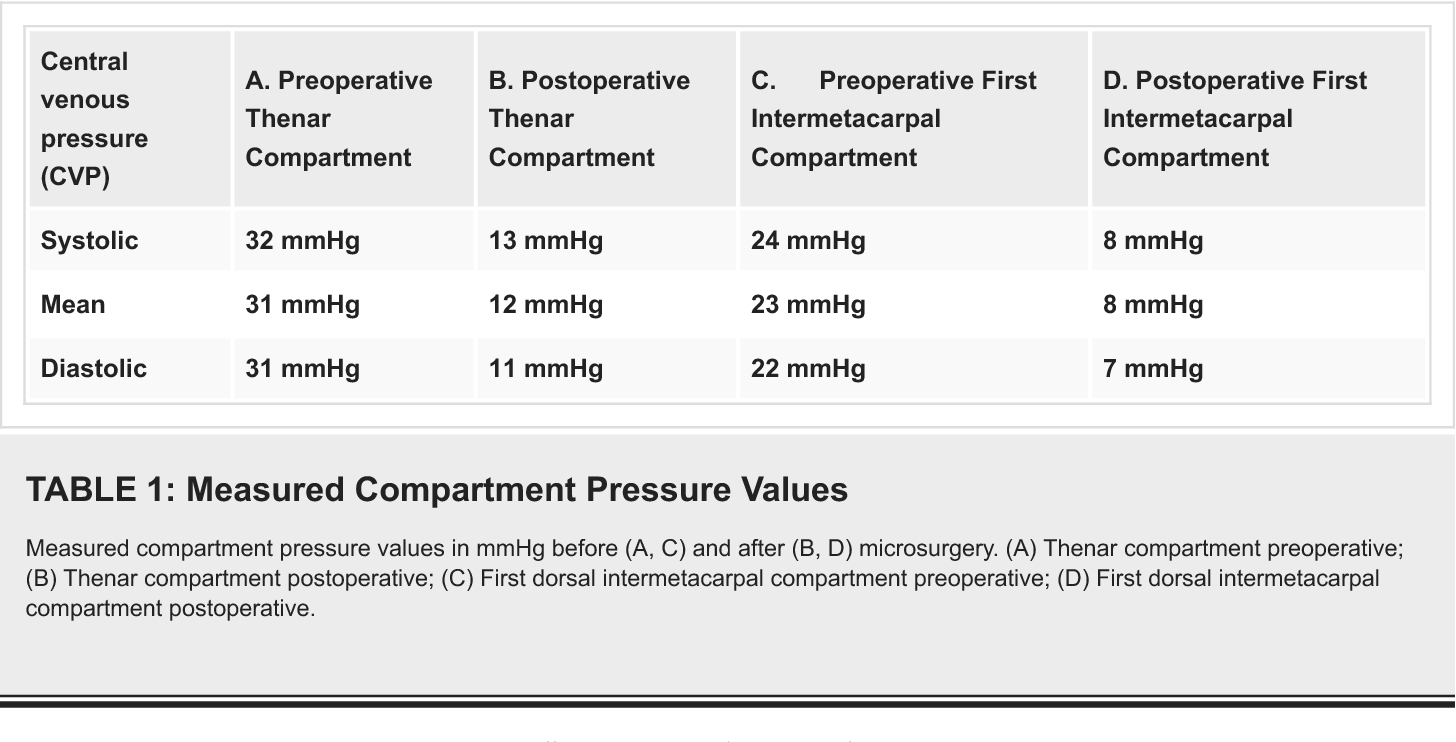
Delta pressure is obtained by subtracting the patients compartment pressure from their diastolic pressure. The estimated sensitivity of intracompartmental pressure monitoring for suspected acute compartment syndrome was 94 with an estimated specificity of 98 an estimated positive predictive value of 93 and an estimated negative predictive value of 99. Zero the assembled unit at the angle you will be entering compartment.
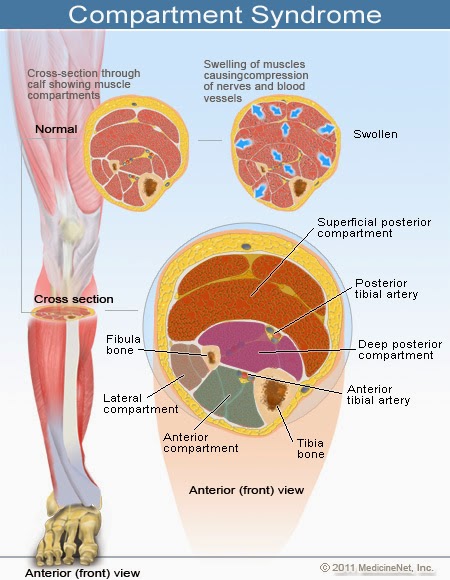
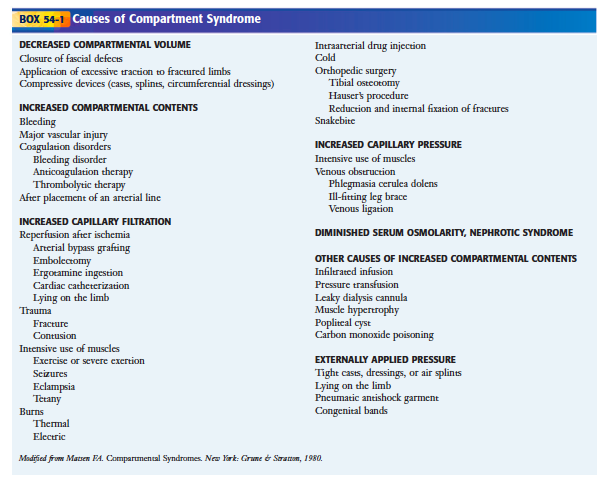
A delta pressure of compartment syndrome 8-10 Additionally many have argued that continuous compartment pressure monitoring is more important than single static measurements as single measurements may lead to unnecessary fasciotomies. S A steady state pressure of greater than 12mmHg concealed within the abdominal cavity S Abdominal Perfusion Pressure APP S Defined as Mean Arterial Pressure MAP Intra-Abdominal Pressure IAP S Abdominal Compartment Syndrome ACS S A. - development of a compartment syndrome depends not only on intra-compartment pressure but also depends on systemic blood pressure.
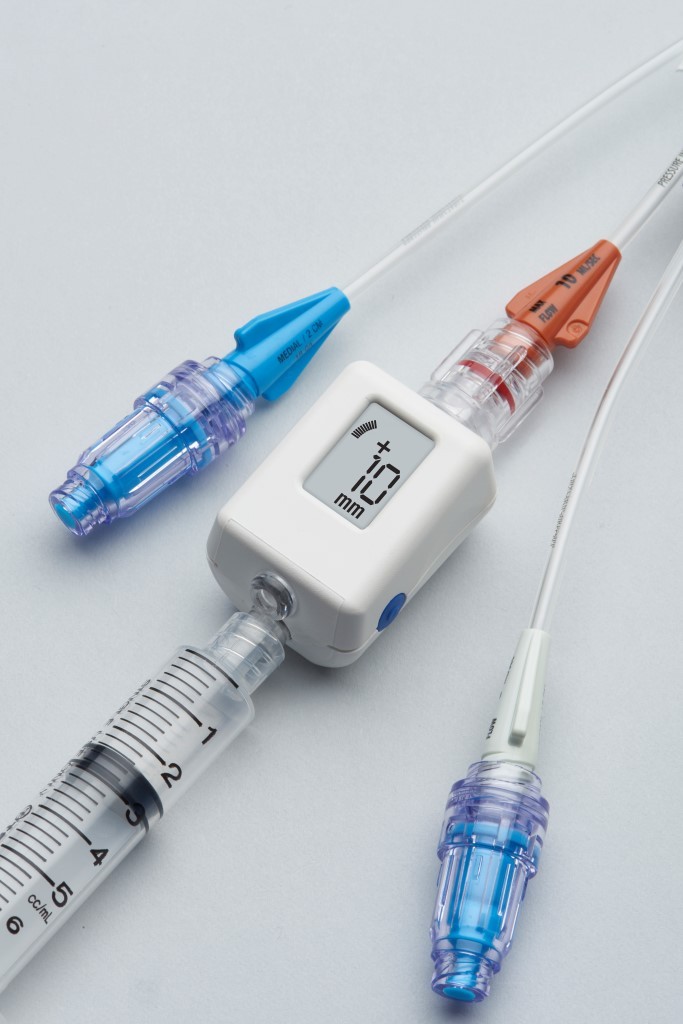
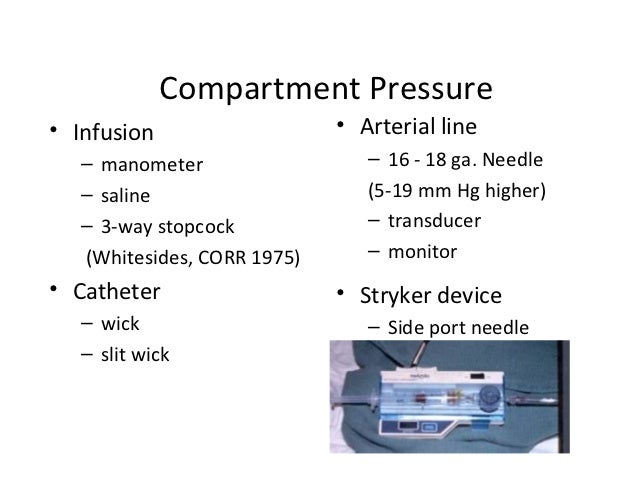
Push the monitoring button to turn it on then hold the monitor at the angle youre going to Stryker at and hold the zero button down. Compartment Syndrome Pressure Monitoring. CPM is mainly of use in the following situations.
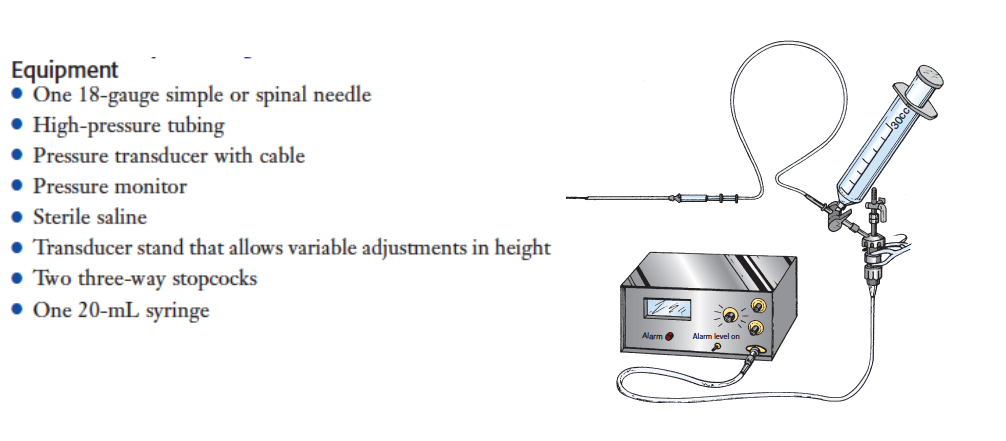
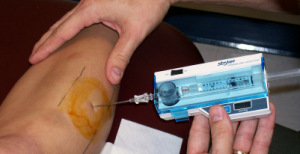
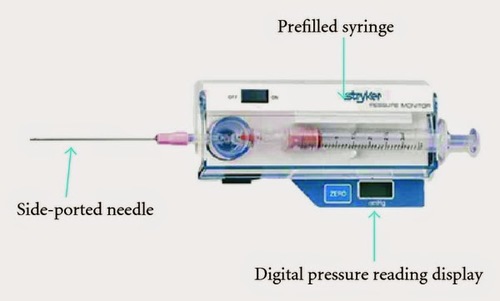
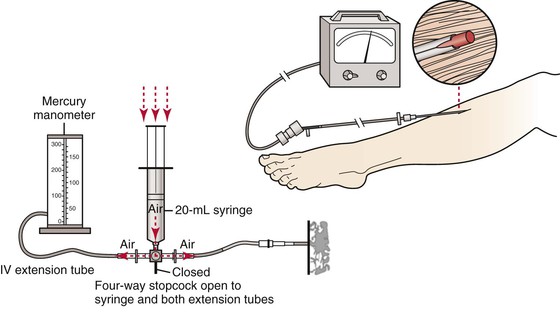
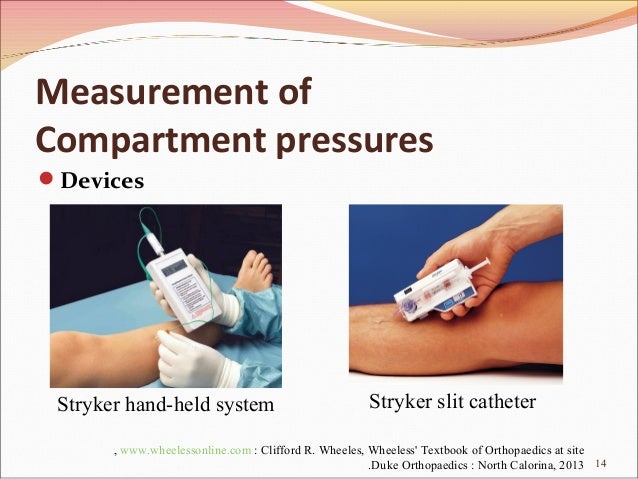
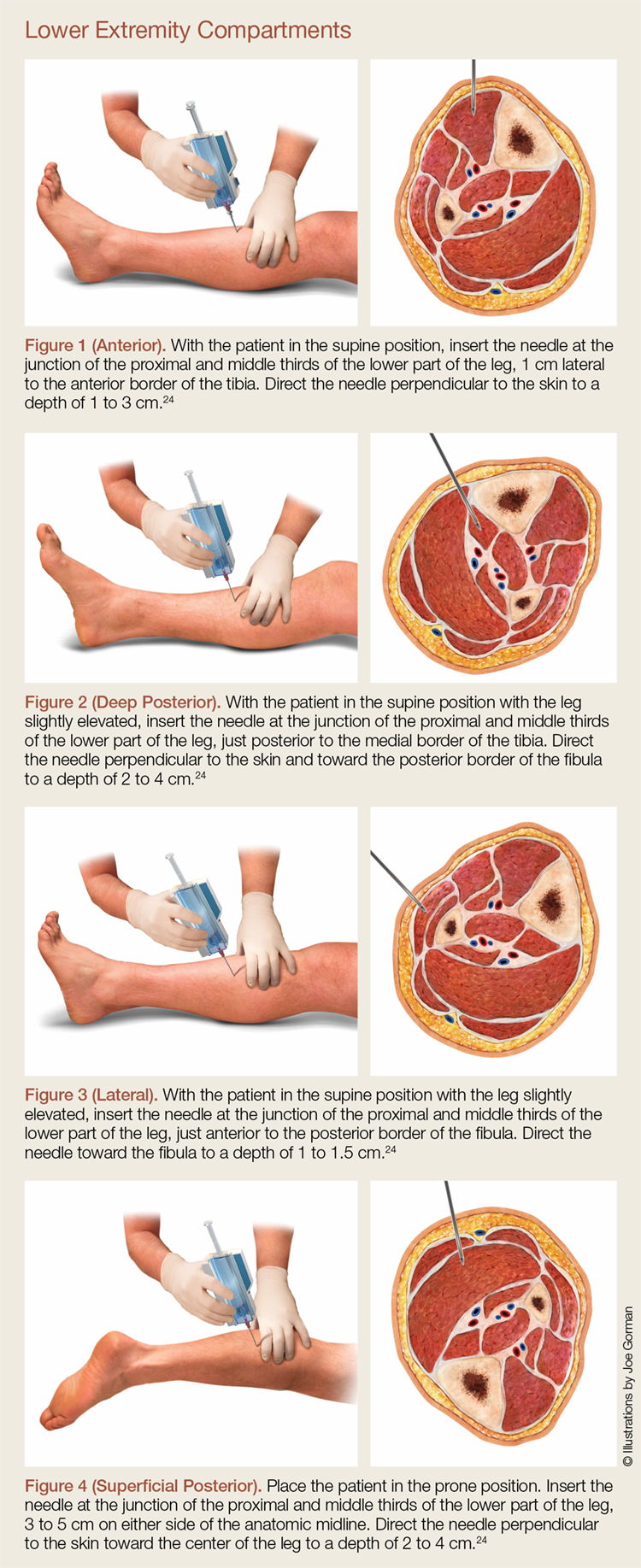
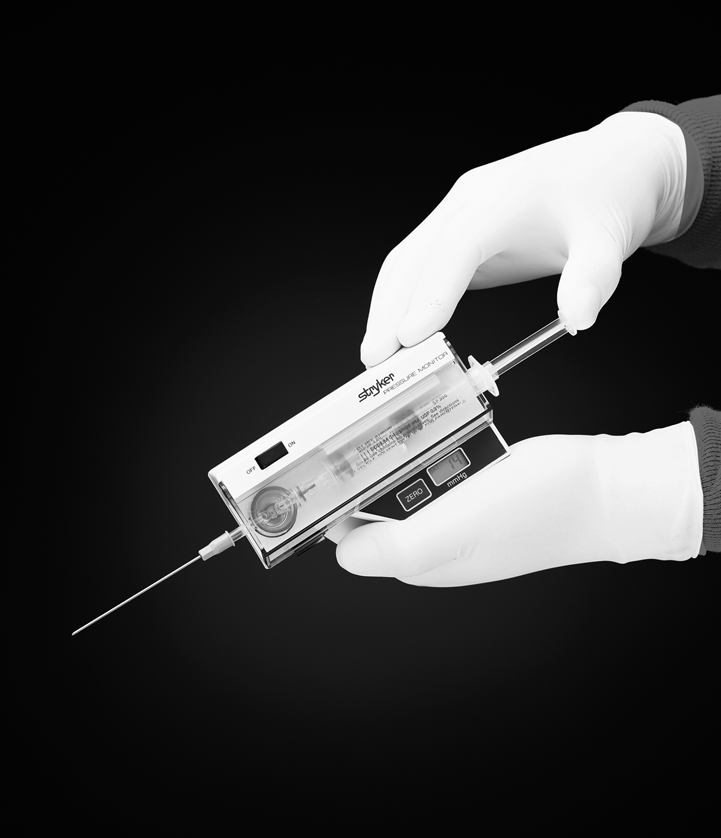
Compartment pressure monitoring Compartment pressure monitoring CPM is not a routine part of the assessment of compartment syndrome. The Stryker system a commercially available instrument is used here. Determine the appropriate site of injection to measure the desired compartment pressure.
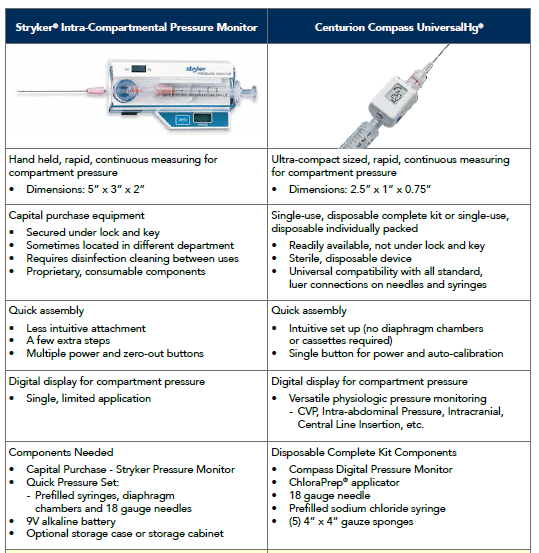
The stryker intra-compartmental pressure monitor system is a convenient self-containedreliable unit for an immediate or continuous reading of compartment pressure. See also Compartment Syndrome.
CPM is mainly of use in the following situations.
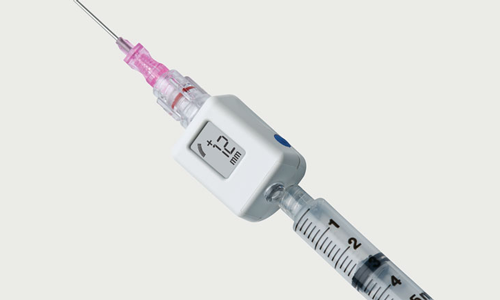
1 Connect probe to monitor Connect the probe to the hand-held monitor. - many surgeon use 30 mm Hg as the cut off for performing fasciotomy. S A steady state pressure of greater than 12mmHg concealed within the abdominal cavity S Abdominal Perfusion Pressure APP S Defined as Mean Arterial Pressure MAP Intra-Abdominal Pressure IAP S Abdominal Compartment Syndrome ACS S A. Know what equipment is available at your particular institution. Compartment Pressure Monitoring Kits. A delta pressure of compartment syndrome 8-10 Additionally many have argued that continuous compartment pressure monitoring is more important than single static measurements as single measurements may lead to unnecessary fasciotomies. In addition to the clinical exam and index of suspicion many surgeons use the delta pressure to help determine the need for fasciotomy. Zero the assembled unit at the angle you will be entering compartment. CPM is mainly of use in the following situations.
S A steady state pressure of greater than 12mmHg concealed within the abdominal cavity S Abdominal Perfusion Pressure APP S Defined as Mean Arterial Pressure MAP Intra-Abdominal Pressure IAP S Abdominal Compartment Syndrome ACS S A. If the diagnosis is clear then the patient must undergo urgent fasciotomies. - development of a compartment syndrome depends not only on intra-compartment pressure but also depends on systemic blood pressure. Delta pressure is obtained by subtracting the patients compartment pressure from their diastolic pressure. 1 Connect probe to monitor Connect the probe to the hand-held monitor. S A steady state pressure of greater than 12mmHg concealed within the abdominal cavity S Abdominal Perfusion Pressure APP S Defined as Mean Arterial Pressure MAP Intra-Abdominal Pressure IAP S Abdominal Compartment Syndrome ACS S A. To check the number of remaining measurements.








.jpg)



















Posting Komentar untuk "Compartment Syndrome Pressure Monitoring"