Down Syndrome Congenital Heart Disease
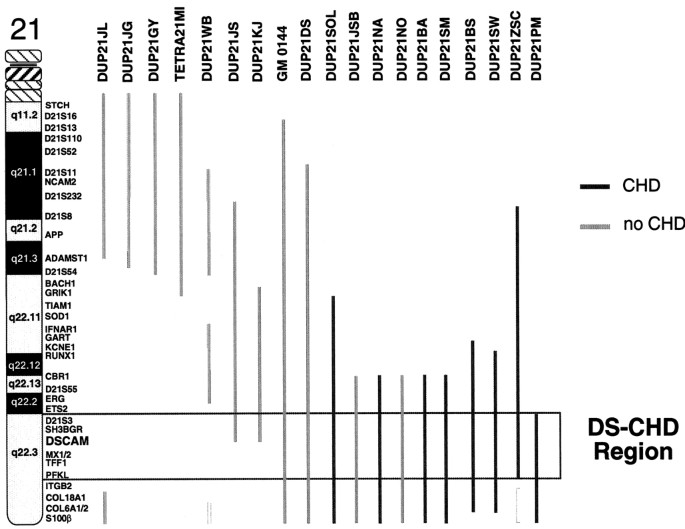
Down syndrome congenital heart disease. Genetics particularly the extra 21st chromosome that all children with Down syndrome have likely play a role in the development of heart defects. Little is known about the cardiovascular phenotype in infants with Down syndrome born today. Down syndrome DS is present.
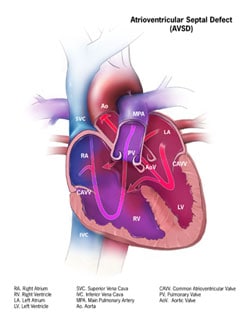
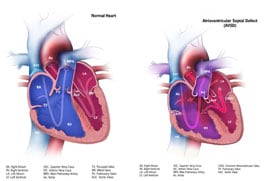
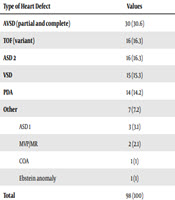
Ventricular Septal Defects VSDs Atrial Septal Defects Patent Ductus Arteriosus Tetralogy of Fallot. Congenital Heart Disease in Children with Down Syndrome Atrioventricular Septal Defects AVSDs These are the most common in children with Down syndrome. ATRIOVENTRICULAR SEPTAL DEFECT AVSD AVSD is the most frequently diagnosed congenital heart condition in children with Down syndrome.
What This Study Adds. Down syndrome DS is a major cause of congenital heart disease CHD and the most frequent known cause of atrioventricular septal defects AVSDs. With the introduction of antenatal screening many fetuses diagnosed with Down syndrome are aborted.
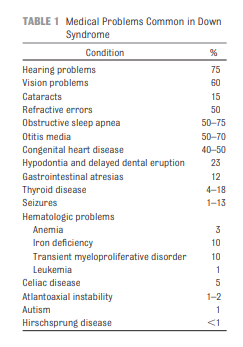
The vast majority of these heart defects require surgical or transcatheter intervention most commonly in infancy. Down syndrome DS is the most common chromosomal abnormality with a prevalence of 118 per 10000 live births 1. Approximately 50 of newborns with DS have congenital heart disease CHD 2 3.
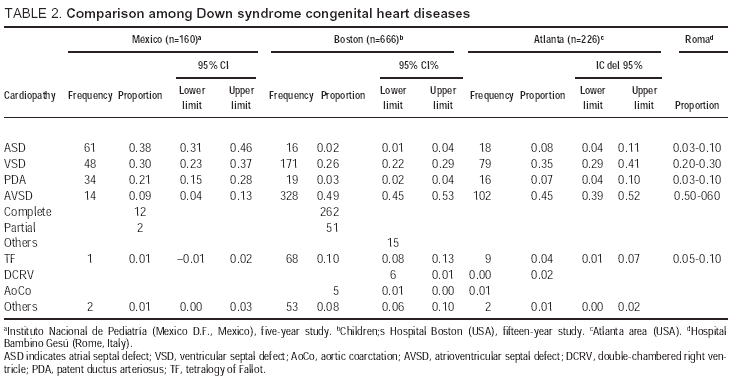
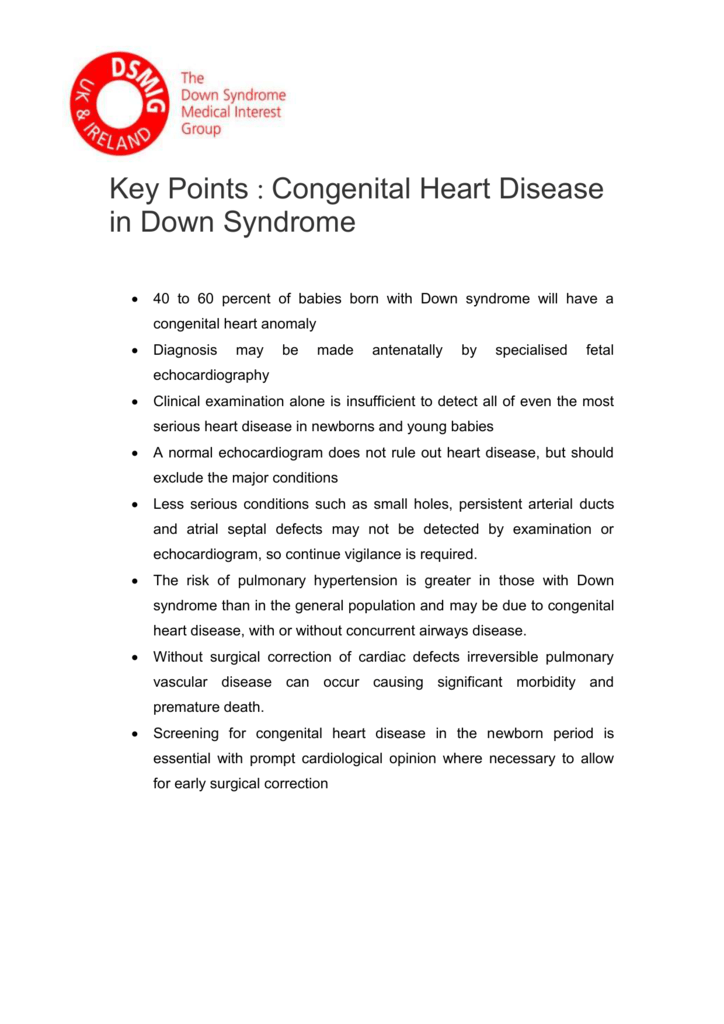
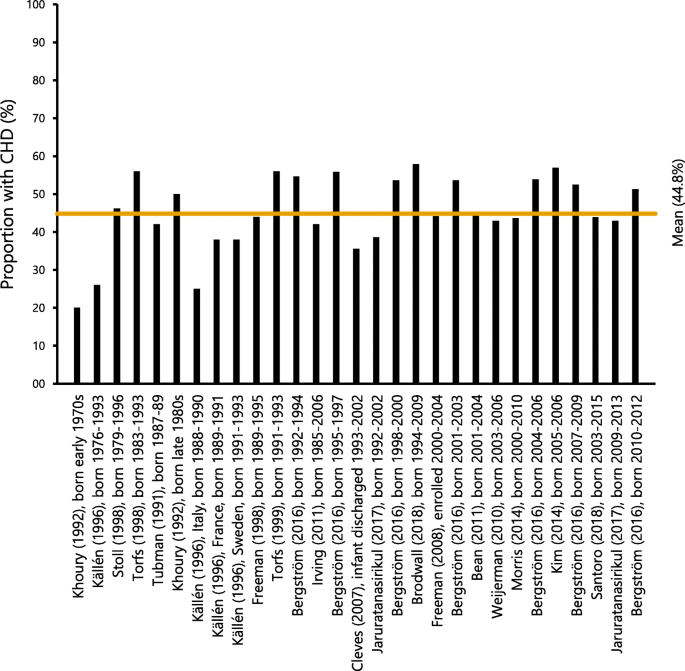
Congenital heart defects CHDs are a major cause of morbidity and mortality in DS patients ranges from 40 to 60. Congenital heart disease CHD is a well-known co-occurring condition in Down syndrome DS. The most common cardiac anomaly ventricular septal defect was found in 49 per cent of the 80 cases studied while the second most frequently encountered anomaly common atrioventricular canal was found in 15.
A physical examination electro cardiogram radiograph of chest and two-dimensional echocardiography was performed on all patients. Congenital heart disease CHD is present in 3550 of patients and is haemodynamically significant in two-thirds. The 5-methyltetrahydrofolate homocysteine methyl transferase reductase MTRR.
About 25 percent of children with a heart defect have one or more additional abnormalities in another organ. Non-cardiac comorbidities may also be present.
Endocardial-cushion-defect was the commonest anomaly followed by ventricular septal defect.
Molecular studies of rare. Congenital heart defects CHDs are a major cause of morbidity and mortality in DS patients ranges from 40 to 60. The incidence of Down syndrome DS has been estimated one case in 814 live births in Iranian population. Endocardial-cushion-defect was the commonest anomaly followed by ventricular septal defect. ATRIOVENTRICULAR SEPTAL DEFECT AVSD AVSD is the most frequently diagnosed congenital heart condition in children with Down syndrome. Congenital heart disease CHD is present in 3550 of patients and is haemodynamically significant in two-thirds. Genetics particularly the extra 21st chromosome that all children with Down syndrome have likely play a role in the development of heart defects. Little is known about the cardiovascular phenotype in infants with Down syndrome born today. Ventricular Septal Defects VSDs Atrial Septal Defects Patent Ductus Arteriosus Tetralogy of Fallot.
Congenital heart defects CHD are the most common abnormalities occurring in 40 -60 of Down syndrome DS patients. The 5-methyltetrahydrofolate homocysteine methyl transferase reductase MTRR. Approximately 50 of newborns with DS have congenital heart disease CHD 2 3. Congenital heart disease in Down syndrome A review of temporal changes Abstract. Three of the most common heart conditions seen in children with Down syndrome are atrioventricular septal defect patent ductus arteriosus and tetralogy of Fallot. Ventricular Septal Defects VSDs Atrial Septal Defects Patent Ductus Arteriosus Tetralogy of Fallot. Congenital heart disease CHD is present in 3550 of patients and is haemodynamically significant in two-thirds.


























31196-9.fp.png)







60789-x.fp.png)

Posting Komentar untuk "Down Syndrome Congenital Heart Disease"